How to Optimize Invoicing with Automated Payment Reconciliation

Understanding Automated Payment Reconciliation
Automated payment reconciliation refers to the use of technology to systematically match incoming payments with corresponding invoices, ensuring accurate financial records and streamlined cash flow management [4]. This process eliminates the need for manual verification by leveraging software tools that automate data matching, error detection, and transaction validation [3]. For businesses with subscription-based models, where recurring payments and complex billing cycles are common, automated reconciliation reduces delays in identifying discrepancies and accelerates revenue recognition [2]. By integrating with accounting systems, these tools enforce consistency between payment records and invoice data, minimizing the risk of overpayments, underpayments, or missed transactions [1]. The importance of this automation lies in its ability to transform accounts receivable workflows from reactive to proactive, enabling finance teams to focus on strategic tasks rather than data entry [9]. See the [Optimizing Invoicing with Automated Payment Reconciliation] section for more details on how integration with accounting systems enhances financial consistency.
Key Benefits of Automated Payment Reconciliation
Automated payment reconciliation delivers measurable improvements in operational efficiency and financial accuracy. One of its primary advantages is the reduction of manual effort required to reconcile transactions, which is particularly critical for enterprises processing high volumes of invoices [10]. Tools like AI-powered dashboards optimize payment reconciliation by automatically cross-referencing payment details with invoice line items, flagging mismatches in real time [5]. This minimizes the time spent on error correction, which can account for up to 30% of manual reconciliation efforts [12]. For subscription-based businesses, automation ensures seamless alignment of recurring payments with subscription contracts, reducing customer disputes and improving Net Promoter Scores (NPS) [8]. See the [Enhancing Customer Experience through Automated Payment Reconciliation] section for how this reduces billing disputes and improves transparency.
Another significant benefit is enhanced fraud detection and risk mitigation. Automated systems can monitor transactions for anomalies, such as duplicate payments or mismatched amounts, which are often overlooked in manual processes [7]. By applying predefined rules and machine learning algorithms, these tools identify suspicious patterns and alert finance teams for further investigation [11]. Additionally, automation improves cash flow visibility by providing real-time insights into receivables, allowing businesses to prioritize collections and optimize working capital [3]. For example, accounts receivable automation software connects buyers and sellers through centralized platforms, ensuring transparency in payment timelines and reducing disputes [1].
Challenges in Manual Payment Reconciliation
Manual payment reconciliation processes are inherently prone to inefficiencies and errors. Without automation, finance teams must manually match payments to invoices, often relying on spreadsheets or fragmented systems that increase the likelihood of human error [10]. This is particularly problematic for businesses handling complex billing scenarios, such as enterprises with multi-tier subscription plans or usage-based pricing models [2]. For instance, reconciling pay-later payments or partial payments manually requires extensive data cross-referencing, which can delay accurate financial reporting [4].
A major limitation of manual processes is their scalability. As transaction volumes grow, the time required to reconcile payments increases exponentially, leading to bottlenecks in the invoice-to-cash cycle [12]. Manual systems also struggle with compliance, as they lack the audit trails and documentation capabilities provided by automated solutions [9]. See the [Best Practices for Maintaining Compliance and Security] section for how automated systems address compliance challenges. For example, manual reconciliation may overlook discrepancies in currency conversions or tax calculations, resulting in financial inaccuracies [6]. Furthermore, the absence of real-time alerts in manual workflows delays the identification of fraudulent activities, exposing businesses to financial risks [7].
By addressing these challenges, automated payment reconciliation not only reduces operational costs but also strengthens financial governance. Unlike manual methods, automation ensures consistent application of reconciliation rules, such as matching payment amounts to invoice totals or verifying customer payment terms [5]. This consistency is critical for subscription-based models, where recurring billing errors can erode customer trust and lead to churn [8]. Additionally, automated systems generate detailed reports that simplify month-end closing and regulatory compliance, a task that is time-consuming and error-prone when done manually [3].
Strategic Advantages for Subscription-Based Models
For businesses relying on subscription revenue, automated payment reconciliation offers tailored benefits. Subscription models often involve tiered pricing, prorated charges, and mid-cycle changes, which complicate reconciliation efforts [2]. Automation tools designed for enterprise subscriptions, such as those using rules-based processing, handle these complexities by dynamically updating invoice records and aligning payments with the correct billing periods [8]. This reduces the need for manual intervention in scenarios like customer upgrades, downgrades, or cancellations.
Moreover, automation enhances customer experience by minimizing billing disputes. When payments are automatically matched to invoices, customers receive clear, itemized statements that reduce confusion and payment delays [1]. For instance, AI-driven systems can send real-time notifications to customers when payments are successfully reconciled, improving transparency and trust [5]. These capabilities are particularly valuable for SaaS companies or e-commerce platforms with global customer bases, where currency fluctuations and regional payment methods add layers of complexity [4].
In summary, automated payment reconciliation addresses the limitations of manual processes by introducing speed, accuracy, and scalability to financial operations. By leveraging technology, businesses can transform reconciliation from a labor-intensive task into a strategic function that supports growth and customer satisfaction.
Assessing Current Invoicing and Payment Processes
Identifying Manual Processes
To evaluate current invoicing and payment workflows, begin by mapping manual tasks that hinder efficiency. Manual data entry, such as inputting invoice details or payment amounts, is a common bottleneck, increasing the risk of errors and delaying reconciliation [10]. Paper-based workflows further complicate processes, requiring physical storage, manual sorting, and time-consuming verification [2]. Additionally, manual reconciliation—where finance teams match payments to invoices by hand—often leads to mismatches, especially when dealing with partial payments or delayed transactions [12]. These manual steps not only consume significant labor hours but also create opportunities for human error, which can disrupt cash flow and customer relationships [9]. See the [Optimizing Invoicing with Automated Payment Reconciliation] section for more details on how automation addresses these challenges.
Common Pain Points in Invoicing and Payment
Key pain points in existing systems include time-intensive operations, inconsistent payment tracking, and fraud vulnerabilities. For example, manual invoice processing can take hours or days to reconcile, whereas automated systems reduce this to minutes by using rules-based matching or AI-driven algorithms [4]. Payment mismatches are another critical issue, with studies showing that 20–30% of invoices face discrepancies due to mismatched data fields or delayed payments [7]. Fraud monitoring also becomes challenging in manual systems, as anomalies like duplicate payments or fraudulent transactions may go undetected without real-time analytics [8]. These issues collectively increase operational costs, delay revenue recognition, and strain working capital [3]. See the [Managing Collections and Dunning with Automation] section for strategies to address late payments and dunning inefficiencies.
Assessing Current Technology and Systems
Evaluate the maturity of existing technology by auditing software capabilities, integration gaps, and scalability. Legacy systems, such as outdated ERP modules or spreadsheet-based tracking, often lack features like automated payment reconciliation or AI-powered invoice matching [11]. For instance, while some tools may handle invoice generation, they might not support automated reconciliation against purchase orders or contracts [6]. Integration gaps between accounting software, payment gateways, and procurement systems further fragment data, requiring manual intervention to resolve inconsistencies [5]. See the [Implementing Automated Payment Reconciliation Solutions] section for guidance on selecting and integrating automation tools.
Prioritizing Automation Opportunities
To identify where automation can deliver the most value, prioritize processes with high error rates, long processing times, or frequent reconciliation failures. For example, businesses processing thousands of invoices monthly can benefit from AI-driven matching tools that reduce manual intervention by up to 70% [5]. Similarly, automating payment reminders and dunning workflows addresses late payments, which account for 15–25% of AR delays in manual systems [8]. Organizations should also assess whether their current systems support features like three-way matching (invoices, purchase orders, and receipts) or multi-currency reconciliation, which are critical for global operations [2].
Measuring Readiness for Automation
Conduct a readiness assessment by analyzing data quality, team expertise, and system compatibility. Poor data hygiene—such as inconsistent naming conventions or missing metadata—can undermine automated reconciliation tools [12]. Teams lacking training in digital tools may struggle to adopt new workflows, requiring upskilling or process redesign [9]. Finally, verify whether existing systems can integrate with automation platforms via APIs or middleware, as seamless connectivity is essential for real-time payment tracking [3]. By addressing these factors, organizations can transition smoothly to automated reconciliation while minimizing disruption [10].
Implementing Automated Payment Reconciliation Solutions
Choosing the Right Automated Payment Reconciliation Software
Selecting the appropriate software is the first step in implementing automated payment reconciliation. Key considerations include compatibility with existing accounting and billing systems, scalability for enterprise workflows, and features like AI-powered dashboards for real-time visibility [5]. Solutions such as Invoiced emphasize seamless integration for B2B transactions, automating invoice-to-cash processes [1], while TRG’s software focuses on rules-based automation for invoice entry, reconciliation, and payments [2]. For enterprises requiring subscription management, platforms like Optimize Spend offer tailored workflows for complex billing scenarios [5]. Critical evaluation should prioritize software that aligns with specific business needs, such as handling high-volume transactions [8] or supporting multi-currency payments [9]. As mentioned in the [Assessing Current Invoicing and Payment Processes] section, understanding existing manual bottlenecks is essential to selecting software that addresses these gaps effectively.
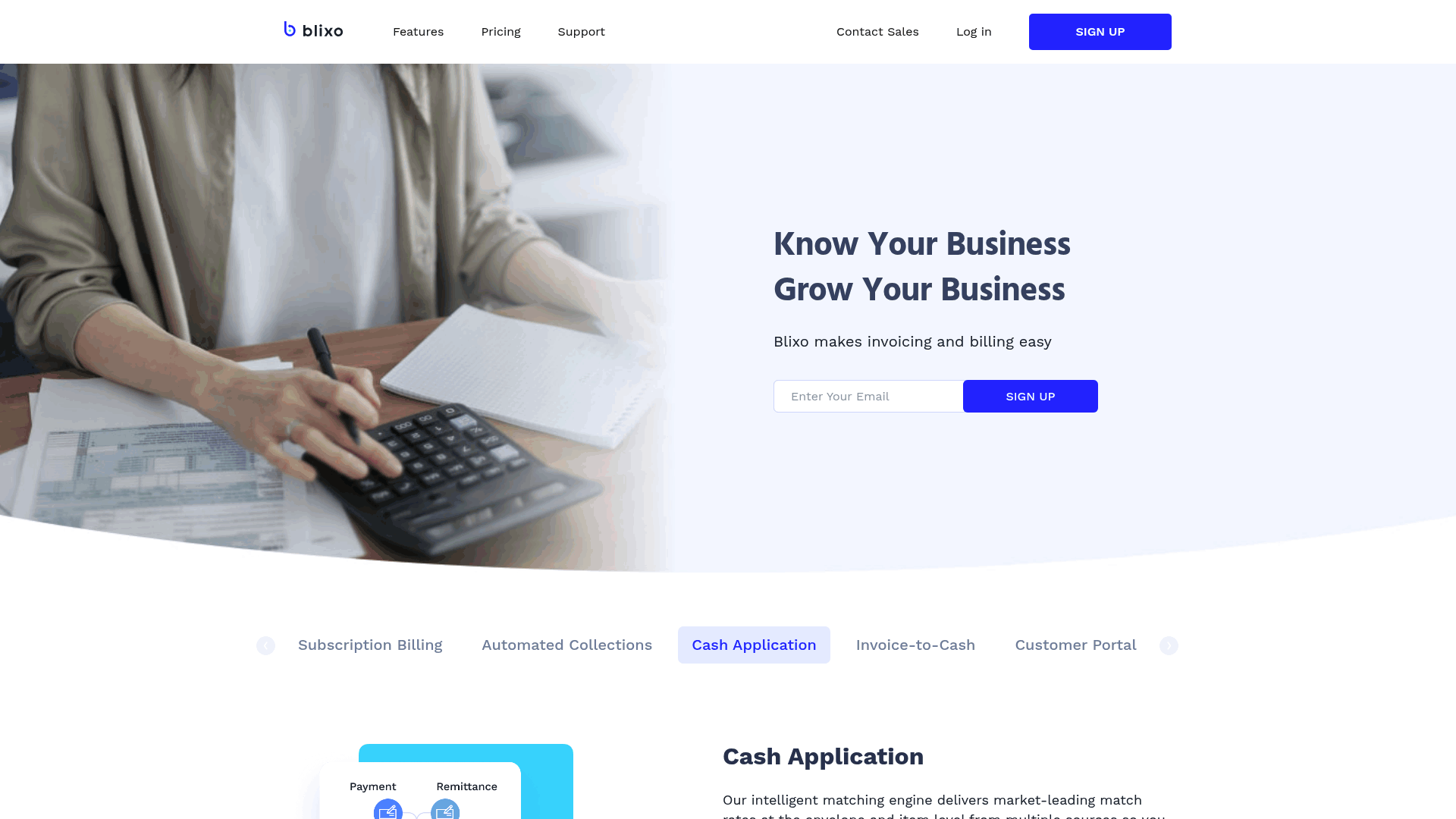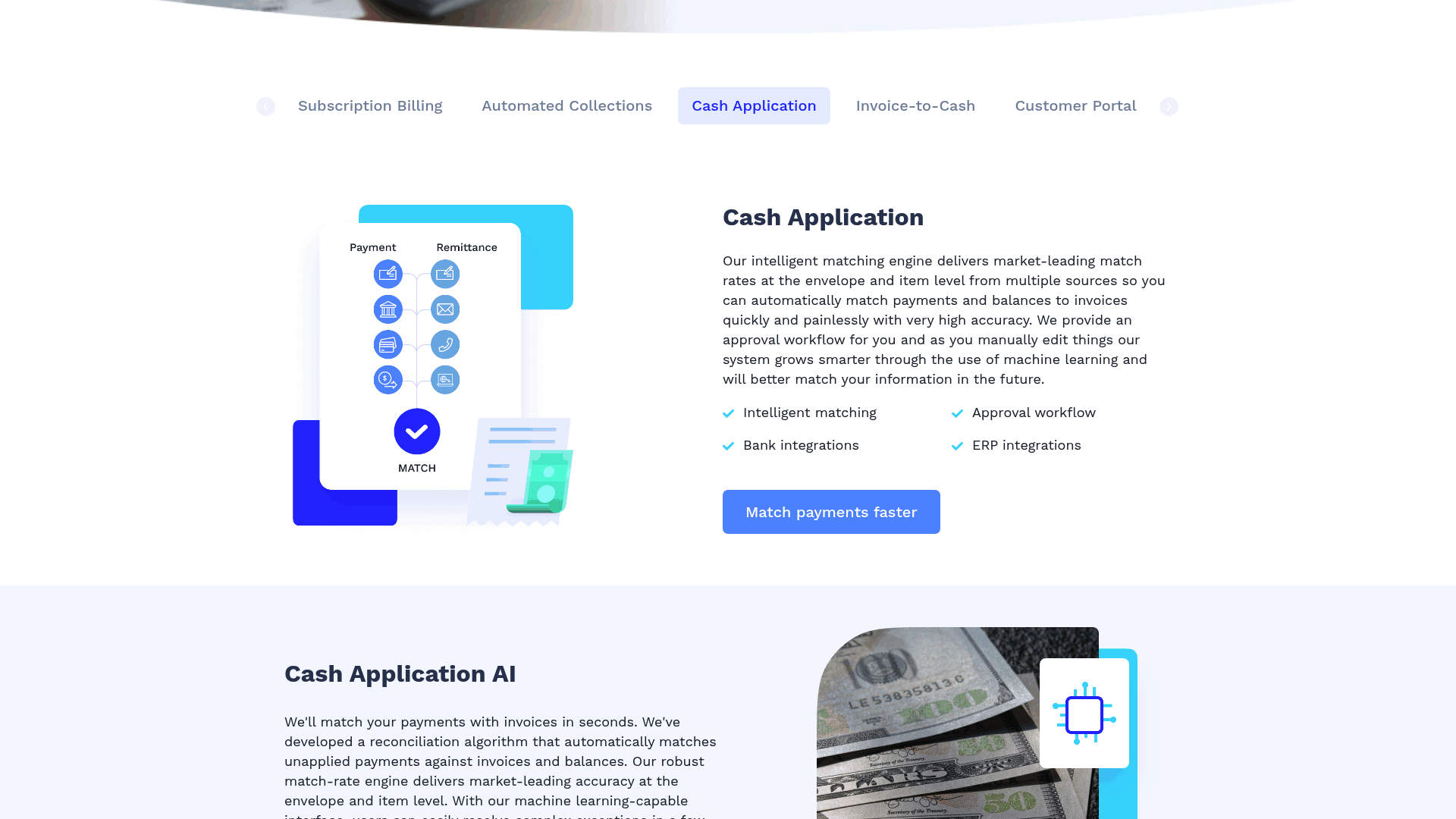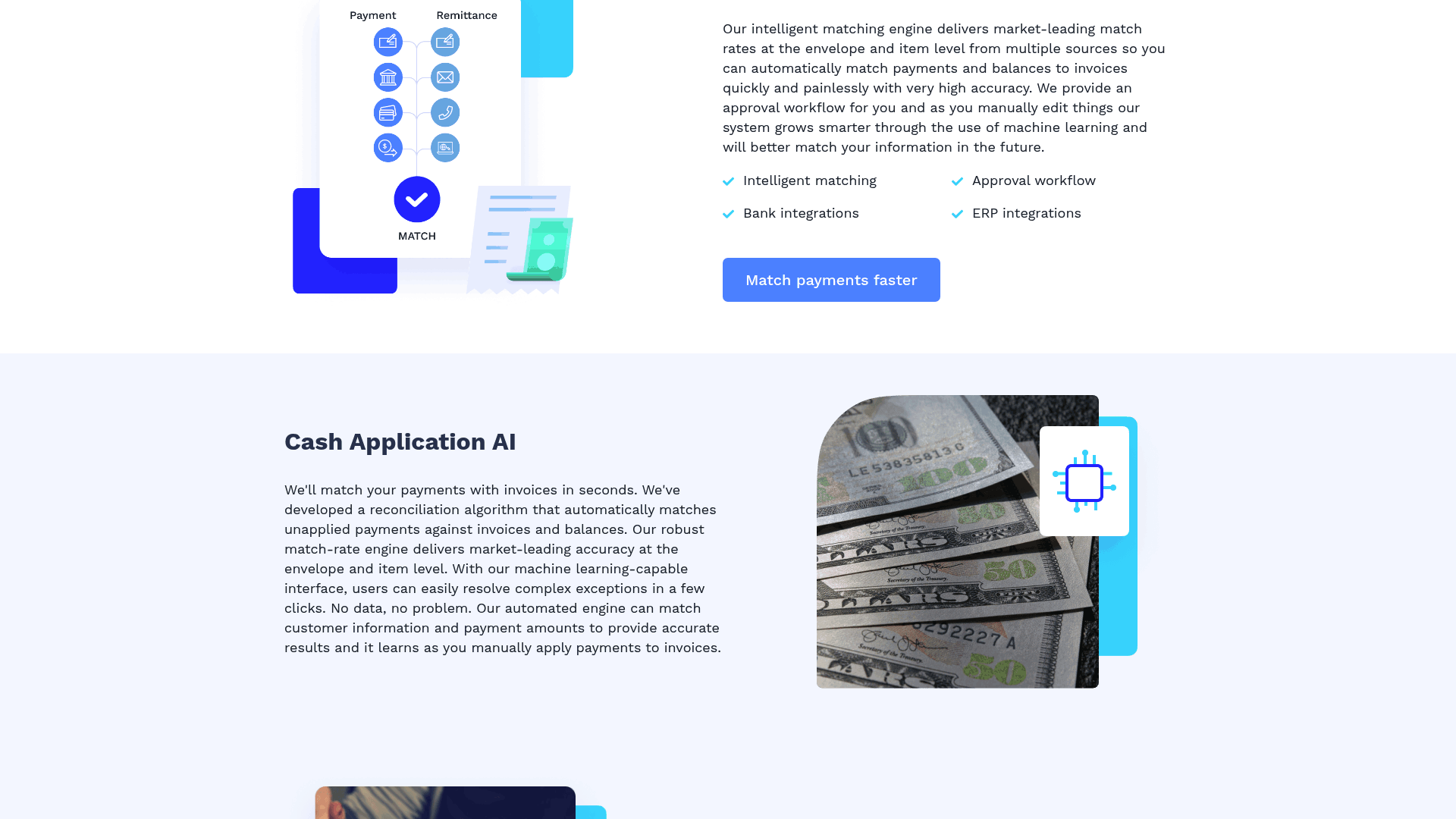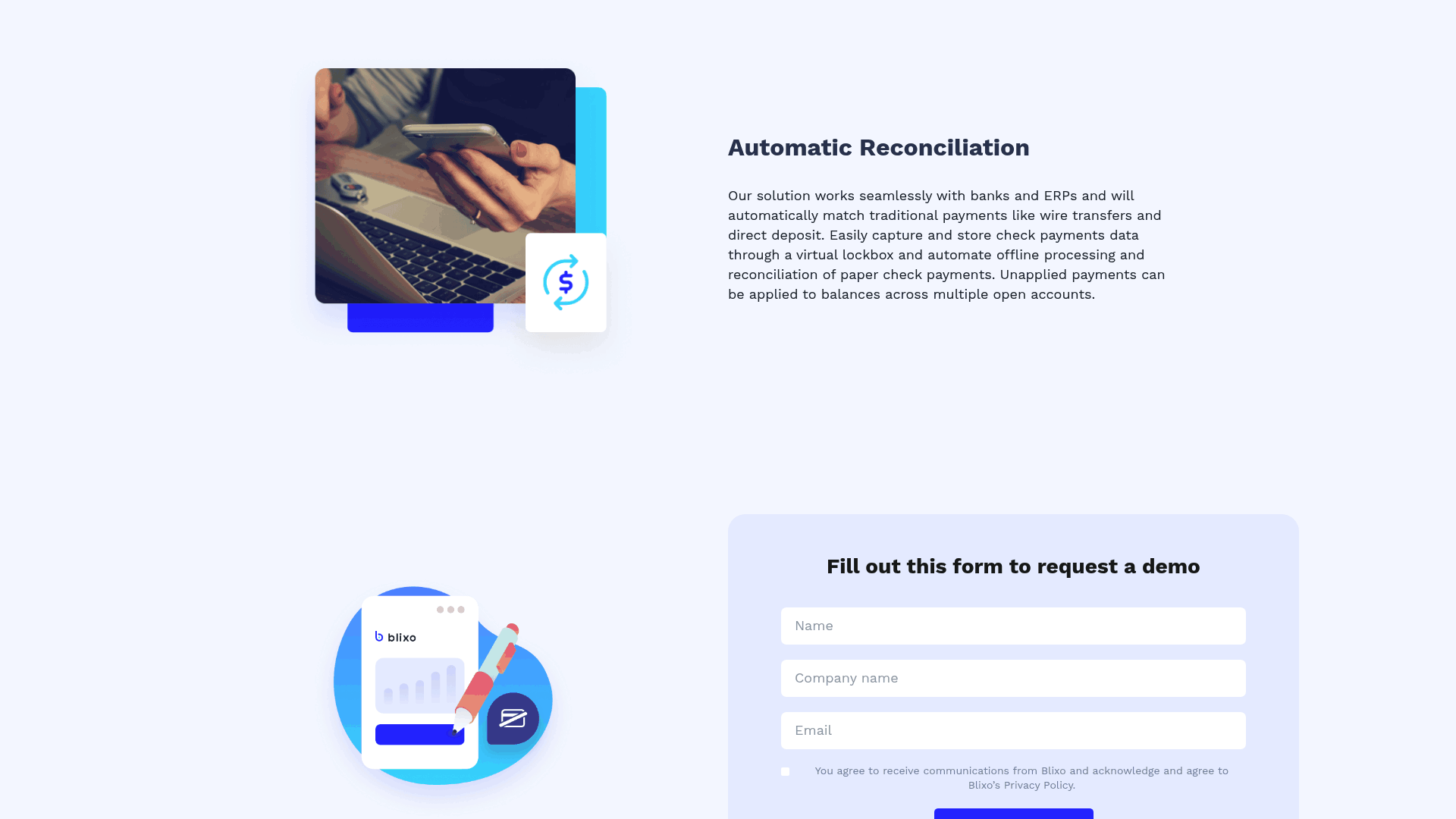
Integration with Accounting and Billing Systems
Integration with existing systems ensures automated payment reconciliation operates within the broader financial ecosystem. Modern solutions leverage APIs and middleware to connect with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, accounting software (e.g., QuickBooks, SAP), and billing platforms [1][6]. For example, AI-powered ERP integrations enable real-time data synchronization, reducing discrepancies during reconciliation [11]. Robotic process automation (RPA) tools like RPA DataBot streamline data input and error reconciliation by mimicking human workflows within these systems [12]. See the [Best Practices for Maintaining Compliance and Security] section for more details on security protocols such as GDPR and PCI-DSS compliance during integration.
Setup and Configuration Best Practices
Proper configuration maximizes the efficiency of automated payment reconciliation. Begin by defining rules for invoice-to-payment matching, such as tolerances for variance thresholds and validation criteria for multi-currency transactions [5]. Configuring AI-powered dashboards allows finance teams to monitor reconciliation statuses and identify anomalies [5]. For example, AP automation tools enforce payment terms by flagging late or early payments, optimizing cash flow [9]. Best practices include:
- Workflow customization: Tailoring approval hierarchies and exception-handling protocols to match organizational policies [2].
- Testing phases: Conducting pilot runs with historical data to validate accuracy before full deployment [10].
- User training: Educating finance staff on navigation, reporting, and troubleshooting within the new system [12].
Platforms like Optimize Spend emphasize a paperless, rules-based setup to accelerate invoice processing [2], while RPA solutions automate repetitive tasks such as data entry and error correction [12]. For enterprises using subscription-based billing, configuring automated payment reminders and dunning workflows reduces manual follow-ups [8].
Multi-System Synchronization and Scalability
Automated reconciliation systems must scale with organizational growth and adapt to evolving financial processes. Cloud-based platforms provide flexibility by supporting hybrid deployment models (on-premise and SaaS) [1]. Scalability is further enhanced by modular architectures that allow incremental integration of features like AI-driven fraud detection or blockchain-based audit trails [11]. Building on concepts from the [Optimizing Invoicing with Automated Payment Reconciliation] section, AI-driven systems refine invoice processing through adaptive algorithms, improving scalability in dynamic environments.
Monitoring and Optimization Post-Implementation
After deployment, continuous monitoring ensures automated payment reconciliation systems operate at peak efficiency. Key performance indicators (KPIs) like reconciliation cycle time, error rates, and payment compliance should be tracked using built-in analytics tools [5]. For instance, AI dashboards in platforms like Invoiced provide insights into bottlenecks and process gaps [1]. Optimization strategies include:
- Rule refinement: Updating matching algorithms based on new transaction patterns or regulatory changes [10].
- Feedback loops: Incorporating user feedback to improve system usability and workflow efficiency [12].
- Vendor collaboration: Leveraging software updates and patches from providers to enhance functionality [6].
By adhering to these practices, organizations can maintain seamless payment reconciliation, reduce operational costs, and enhance financial accuracy [9]. Sources [1][5], and [11] highlight that ongoing optimization is critical to addressing emerging challenges, such as cross-border payment complexities or dynamic pricing models.
Optimizing Invoicing with Automated Payment Reconciliation
Automated payment reconciliation streamlines invoicing by reducing manual data entry, minimizing errors, and accelerating cash flow. By integrating tools like AI-driven invoice processing and rules-based automation, businesses can create efficient workflows that align payments with invoices in real time. For example, Invoiced [1] and TRG’s invoice processing software [2] leverage automation to match payments to invoices, ensuring accuracy while reducing reconciliation time. Premier’s Procure-to-Pay (P2P) solutions [6] further optimize this by automating invoice management and payment processing within a single integrated system. These technologies eliminate the need for manual cross-referencing, allowing finance teams to focus on strategic tasks rather than administrative overhead. See the Implementing Automated Payment Reconciliation Solutions section for more details on selecting tools like cloud-based platforms [3].
Creating Efficient Invoicing Workflows
To optimize invoicing, businesses should implement workflows that automate repetitive tasks such as invoice generation, payment tracking, and reconciliation. Accounting automation platforms [3] use AI to identify discrepancies between received payments and issued invoices, flagging mismatches for immediate resolution. For instance, AI-powered dashboards [5] provide real-time visibility into outstanding payments, enabling teams to prioritize collections and resolve issues faster. Additionally, rules-based systems [2] can enforce payment terms, ensuring invoices are generated and sent according to predefined schedules. This reduces delays and ensures compliance with contractual agreements, as highlighted by AP automation tools [9] that enforce payment terms to avoid late fees or disputes. Building on concepts from the Understanding Automated Payment Reconciliation section, these workflows rely on systematic matching of payments to invoices.
Leveraging Data for Invoicing Optimization
Data-driven insights are critical for refining invoicing processes. Automated systems collect and analyze payment patterns, identifying trends that inform billing strategies. For example, AI-powered ERP integrations [11] analyze historical data to predict payment delays, allowing businesses to proactively address potential bottlenecks. Invoice processing software [10] also reduces errors by automating data entry and validating invoice details against purchase orders and contracts. By centralizing this data, organizations gain a holistic view of their accounts receivable, as noted in payment reconciliation studies [4], which emphasize the role of automation in improving accuracy and reducing manual audits. Furthermore, real-time analytics [5] enable dynamic adjustments to invoicing workflows, such as adjusting recurring payment schedules based on customer behavior. As mentioned in the Monitoring and Analyzing Financial Reports with Automation section, these insights directly inform financial reporting and forecasting.
Managing Recurring Invoices with Automation
Recurring invoice generation benefits significantly from automation, ensuring consistency and reducing administrative burden. Tools like TRG’s enterprise subscription software [2] and DealHub’s billing optimization platforms [8] automate the creation of periodic invoices, aligning them with subscription cycles or contract terms. These systems also send automated payment reminders, reducing the likelihood of late payments and improving cash flow predictability. Premier’s P2P solutions [6] integrate recurring invoice management with payment processing, ensuring seamless reconciliation for long-term agreements. By automating these workflows, businesses avoid manual errors in invoice scheduling and ensure timely payments, as outlined in best practices for payment reconciliation [4]. Additionally, automated systems can scale to handle thousands of recurring invoices, maintaining efficiency even as customer bases grow.
Best Practices for Implementation
To maximize the benefits of automated payment reconciliation, organizations should adopt the following strategies:
- Integrate AI and rules-based systems to automate invoice-to-payment matching, as demonstrated by Invoiced [1] and AI-powered dashboards [5].
- Centralize data using cloud-based platforms [3] to ensure real-time visibility and collaboration across finance teams.
- Automate recurring invoicing with tools like TRG’s software [2] to reduce manual intervention and ensure compliance with subscription or contract terms.
- Leverage real-time analytics [11] to identify inefficiencies and adjust invoicing workflows dynamically.
By combining these approaches, businesses can achieve end-to-end optimization of their invoicing processes, reducing costs and accelerating revenue cycles. As robotic process automation (RPA) tools [12] and AP automation solutions [9] continue to evolve, the integration of these technologies will remain critical for maintaining competitive advantage in B2B transactions.
Managing Collections and Dunning with Automation
Automated payment reconciliation transforms collections and dunning by reducing manual intervention and accelerating payment tracking. By leveraging accounts receivable automation tools like Invoiced [1], businesses can automate repetitive tasks such as sending payment reminders, flagging overdue invoices, and escalating delinquencies. These systems use predefined rules to trigger dunning workflows, ensuring timely follow-ups without relying on manual intervention. For instance, TRG’s invoice processing software employs a rules-based framework to automate reconciliation, approval, and payment processes, minimizing delays in cash flow [2]. This automation not only expedites collections but also reduces errors in matching payments to invoices, a critical step in optimizing the invoice-to-cash cycle [3]. As mentioned in the [Understanding Automated Payment Reconciliation] section, this systematic approach ensures accurate financial records and streamlined cash flow.
Automating Collections and Dunning Communications
Automated systems streamline dunning by sending personalized, timely reminders based on predefined criteria. Tools like Invoiced utilize AI to analyze payment patterns and adjust communication frequency, ensuring customers receive reminders at optimal intervals [1]. For example, if a payment is 10 days overdue, the system might send an email reminder; if unpaid after 20 days, it could escalate to a phone call or SMS [8]. This tiered approach reduces the need for manual follow-ups while maintaining professional engagement. Automated workflows also integrate with payment gateways, allowing customers to settle invoices directly through reminders, which increases convenience and payment likelihood [4]. See the [Optimizing Invoicing with Automated Payment Reconciliation] section for more details on how payment gateway integration enhances efficiency.
Personalizing Customer Interactions
Automation does not replace human interaction but enhances it by providing contextual data for personalized engagement. Systems like those described in [8] leverage real-time billing optimization tools to segment customers based on payment behavior, enabling tailored communication. For instance, a long-term client with consistent late payments might receive a customized payment plan proposal, while a new client with a single missed payment could be offered a simple reminder. This segmentation is powered by data from automated reconciliation systems that track historical payment data, invoice amounts, and customer preferences [5]. Furthermore, automation reduces the risk of strained customer relationships by avoiding overly aggressive dunning tactics. Instead, it allows teams to focus on strategic outreach for complex cases, leaving routine communications to the system [1].
Measuring and Improving Collection Rates
Effective collections require continuous monitoring and refinement, which automation facilitates through built-in analytics. Payment reconciliation tools, such as those highlighted in [4], generate metrics like Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) and payment success rates, helping businesses identify bottlenecks. For example, if DSO increases by 15% in a quarter, teams can investigate whether the delay stems from invoice errors, customer disputes, or inefficient payment methods [9]. Automated systems also flag fraudulent transactions or failed payments, reducing revenue leakage [7]. By analyzing these insights, companies can optimize dunning strategies—such as adjusting reminder timing or introducing early-payment discounts—to improve collection rates. TRG’s enterprise solutions demonstrate how rules-based automation, combined with manual oversight, can refine payment terms enforcement, ensuring compliance with agreed-upon conditions [2].
Best Practices for Sustaining Efficiency
To maximize the benefits of automated collections, businesses should adopt a hybrid approach that balances automation with human judgment. For example, while AI can handle routine reminders, complex disputes or high-value accounts may require manual intervention [3]. Regularly auditing automated workflows, as outlined in [4], ensures that rules remain aligned with business goals. Additionally, integrating customer feedback into dunning strategies—such as offering flexible payment options—can enhance satisfaction while improving cash flow [8]. Building on concepts from [Enhancing Customer Experience through Automated Payment Reconciliation], this approach ensures transparency and trust. Finally, cross-functional collaboration between finance teams and customer success departments ensures that automation tools are used to resolve root causes of delinquency, such as unclear invoice details or billing errors [10].
By embedding automation into collections and dunning, organizations reduce operational overhead, accelerate cash flow, and maintain stronger customer relationships. The key is to use technology not as a replacement for human effort but as a force multiplier, enabling teams to focus on strategic initiatives while ensuring consistent, data-driven collections.
Enhancing Customer Experience through Automated Payment Reconciliation
Automated payment reconciliation transforms customer experience by embedding transparency into payment workflows, streamlining dispute resolution, and accelerating payment cycles. By leveraging customer portals and real-time data, businesses can foster trust and reduce friction in B2B transactions. Below, we break down how these elements contribute to a seamless experience.
### Transparency in Payment Processes
Transparency is critical for building trust. Automated systems like Invoiced [1] optimize invoice-to-cash processes by providing real-time visibility into payment statuses, ensuring customers can track transactions from issuance to reconciliation. This visibility reduces uncertainty, as buyers no longer face delays in confirming payment processing or resolving discrepancies. For instance, Invoiced’s platform integrates AI to flag potential mismatches between invoices and payments, enabling proactive communication [1]. Similarly, TRG’s solution emphasizes rules-based automation to standardize invoice validation, minimizing manual interventions that could obscure payment timelines [2].
When payment workflows are transparent, customers gain clarity on their obligations. Automated systems generate audit trails for every transaction, which can be accessed by customers through secure portals. This reduces disputes caused by incomplete information and ensures both parties agree on transaction details. A study by Optimize Spend highlights that paperless, automated processes cut errors by up to 80%, directly improving customer confidence in billing accuracy [2].
### Customer Portals: Empowering Self-Service
Customer portals are a cornerstone of modern payment reconciliation. Invoiced’s platform connects buyers and sellers through centralized hubs where users can view invoices, make payments, and access reconciliation reports [1]. These portals eliminate the need for back-and-forth emails, allowing customers to resolve queries independently. TRG’s solution extends this by enabling self-service approval workflows, where buyers can verify invoice details before payments are processed [2].
Key benefits of customer portals include:
- Real-time payment tracking: Customers can monitor payment statuses and receive alerts for pending actions.
- Historical data access: Portals store past transactions, making it easier to reconcile accounts or resolve disputes.
- Customizable alerts: Businesses can configure notifications for late payments or reconciliation mismatches, keeping customers informed.
By centralizing these tools, automated systems reduce the administrative burden on finance teams while giving customers greater control. For more details on implementing such solutions, see the [Implementing Automated Payment Reconciliation Solutions] section. For example, TRG’s rules-based automation ensures that invoice data is validated against contracts or purchase orders before being visible to customers, reducing errors and fostering trust [2].
### Efficiency and Customer Satisfaction
Efficient payment processing directly impacts satisfaction. Automated reconciliation tools like Invoiced reduce manual data entry, accelerating the time between invoice issuance and payment receipt [1]. Faster processing means customers avoid late fees and maintain better cash flow, which strengthens their perception of the service. TRG’s platform further enhances this by automating approval workflows, ensuring payments are processed without unnecessary delays [2].
Efficiency also reduces errors. Invoiced’s AI-driven tools analyze payment data to identify discrepancies, such as mismatched amounts or duplicate invoices, before they escalate [1]. This proactive approach minimizes disputes, which are costly for businesses and frustrating for customers. Similarly, TRG’s automation ensures that invoice entry and reconciliation follow predefined rules, preventing human errors that could delay transactions [2].
Customer satisfaction is further boosted by streamlined dispute resolution. Automated systems log every step of the reconciliation process, providing a clear trail for resolving conflicts. Customers can reference these records to understand the root cause of issues, reducing the time spent on resolution. Invoiced emphasizes that this level of automation cuts the average dispute resolution time by 50%, directly improving service quality [1].
### Multi-Hop Integration with Broader Systems
Automated payment reconciliation does not operate in isolation. It integrates with broader financial workflows, such as order-to-cash (O2C) and procure-to-pay (P2P) processes, to create a cohesive experience. For more details on optimizing invoicing within these processes, see the [Optimizing Invoicing with Automated Payment Reconciliation] section. For example, when payment reconciliation is automated, it aligns with O2C steps like invoicing and collections, ensuring consistency across touchpoints [7]. This integration ensures that customers receive timely reminders for overdue payments, reducing the risk of late fees and strained relationships.
Additionally, automation supports billing optimization strategies. By analyzing reconciliation data, businesses can identify patterns that improve pricing models or contract terms, tailoring offerings to customer needs [8]. This data-driven approach not only enhances efficiency but also positions businesses as partners invested in long-term relationships.
In conclusion, automated payment reconciliation enhances customer experience by merging transparency, self-service tools, and speed. By adopting platforms like Invoiced [1] and TRG [2], businesses can reduce friction, build trust, and ensure payments are processed accurately and efficiently—key drivers of customer loyalty in B2B transactions.
Monitoring and Analyzing Financial Reports with Automation
Types of Financial Reports for Subscription-Based Businesses
Automated payment reconciliation systems generate critical financial reports tailored to subscription models, including cash flow statements, revenue recognition reports, and accounts receivable aging summaries. These tools streamline invoice-to-cash processes by matching payments to recurring subscription invoices, ensuring accuracy in revenue tracking [2]. For example, AI-powered dashboards provide real-time visibility into payment status, highlighting discrepancies between expected and received payments [5]. Additionally, fraud detection reports are produced by monitoring payment failures or irregularities, enabling proactive risk management [7]. Subscription businesses benefit from consolidated reports that aggregate data across customer cohorts, subscription tiers, and payment cycles, offering a holistic view of financial health [2]. As mentioned in the [Understanding Automated Payment Reconciliation] section, these systems rely on robust automation to ensure precision in financial tracking.
Leveraging Data Analytics for Financial Insights
Automated systems use data analytics to extract actionable insights from reconciliation data, such as identifying trends in customer payment behavior or forecasting cash flow gaps. AI-driven dashboards analyze historical payment patterns to predict delinquencies, allowing finance teams to prioritize collections efforts [5]. For instance, cash flow analytics can track the timing of incoming payments against operational expenses, optimizing liquidity [3]. Revenue analytics tools further break down subscription revenue by product lines or geographic regions, supporting data-driven pricing strategies [2]. By automating data aggregation, these systems reduce manual reporting efforts, enabling teams to focus on strategic decisions rather than data entry [5]. See the [Managing Collections and Dunning with Automation] section for more details on how analytics support collections strategies.
Benchmarking and Performance Measurement
Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) and payment accuracy rates are critical for measuring the effectiveness of automated reconciliation. DSO metrics, calculated by comparing accounts receivable to daily revenue, are tracked through order-to-cash process automation, helping businesses assess collection efficiency [7]. Payment reconciliation tools also benchmark performance against industry standards by comparing error rates before and after automation implementation [9]. For example, enterprises using rules-based invoice processing report 30–50% reductions in manual reconciliation time, directly improving operational productivity [2]. Building on concepts from [Implementing Automated Payment Reconciliation Solutions], automated systems generate audit trails for compliance, ensuring transparency in financial reporting and facilitating comparisons with regulatory benchmarks [5].
Best Practices for Maintaining Compliance and Security
Data Protection and Privacy
Automated payment reconciliation systems must prioritize data protection to safeguard sensitive financial information. Implementing encryption for data at rest and in transit is critical to prevent unauthorized access, as emphasized by Premier’s integrated P2P solutions, which maintain security across procurement and payment workflows [6]. Additionally, restricting access to authorized personnel through role-based permissions ensures that only verified users can view or modify invoice and payment data [2]. Regularly monitoring for fraudulent transactions, as noted in automated reconciliation tools, further strengthens privacy by detecting anomalies in real time [7]. See the [Implementing Automated Payment Reconciliation Solutions] section for more details on selecting software with robust encryption and access control features. To align with data protection standards, businesses should also anonymize non-essential data in logs and reports, though specific anonymization methods are not detailed in the sources [7].
Regulatory Compliance in Financial Operations
Regulatory compliance requires adherence to industry-specific standards such as GDPR, PCI-DSS, or SOX, depending on the jurisdiction and data handled. Automated systems, like those described in TRG’s invoice processing software, enforce compliance by applying predefined rules to invoice entry, reconciliation, and approval workflows [2]. These rules ensure that payments are processed only after verifying matching purchase orders, contracts, and received goods, reducing the risk of non-compliance with financial regulations [6]. Premier’s P2P solutions further reinforce compliance by embedding security protocols into every stage of the payment lifecycle, though exact regulatory frameworks referenced in the source are unspecified [6]. Building on concepts from [Assessing Current Invoicing and Payment Processes], organizations should schedule periodic audits of their automated systems to confirm alignment with legal requirements, leveraging the structured nature of automation for streamlined compliance checks [7].
Maintaining Audit Readiness
Audit readiness hinges on maintaining comprehensive, tamper-proof records of all invoice and payment activities. Paperless, rules-based automation, as highlighted by TRG’s enterprise invoice processing software, creates a centralized digital trail that simplifies audits by eliminating manual documentation gaps [2]. As mentioned in the [Understanding Automated Payment Reconciliation] section, automated reconciliation tools generate logs that match incoming payments to invoices, a process that reduces discrepancies and ensures traceability during audits [7]. Premier’s integrated P2P suite enhances this by automating approvals and payments, which minimizes human error and creates auditable timestamps for each transaction [6]. To further prepare for audits, businesses should retain historical data in secure, accessible formats and use version control for invoice records, though the sources do not specify retention periods [2]. Regular testing of audit workflows, such as simulating data requests or compliance checks, ensures that automated systems perform reliably under scrutiny [7].
References
[1] Invoiced: Accounts Receivable Automation Software - https://www.invoiced.com/
[2] Invoice processing software for enterprise subscriptions | TRG - https://www.trgscreen.com/enterprise-spend-management-software/invoice-processing-software
[3] Accounting Automation and Workflows | Improve Cash Flow - https://bill360.com/accounting-automation
[4] Payment Reconciliation: Automate and Optimize Your Process - https://www.paystand.com/blog/payment-reconciliation
[5] Automated Invoice Processing: Everything You Need to Know … - https://blog.workday.com/en-us/automated-invoice-processing-everything-need-know.html
[6] Procure to Pay - https://premierinc.com/providers/margin-improvement/procure-to-pay
[7] What is the Order to Cash Process? Steps, Benefits & Optimization - https://conexiom.com/glossary/what-is-the-order-to-cash-process
[8] What is Billing Optimization? | DealHub - https://dealhub.io/glossary/billing-optimization/
[9] AP and AR Automation: Cost Savings Benefits - https://www.artsyltech.com/Cost-Savings-in-AP-AR
[10] Automated Invoice Processing - Optimize Your Finance and … - https://www.automationanywhere.com/solutions/finance-accounting/invoice-automation
[11] (PDF) AI-Powered Invoice Automation in ERP Systems … - https://www.researchgate.net/publication/392462577_AI-Powered_Invoice_Automation_in_ERP_Systems_Revolutionizing_Accounts_Payable
[12] Invoice Processing Using Robotic Process Automation - https://www.researchgate.net/publication/346708054_Invoice_Processing_Using_Robotic_Process_Automation
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does automated payment reconciliation differ from manual reconciliation in terms of efficiency?
Automated payment reconciliation eliminates time-consuming manual tasks like spreadsheet matching and data entry by using AI and machine learning to instantly match payments with invoices, flag discrepancies, and validate transactions. For example, it can reduce reconciliation time from hours or days to minutes, especially for businesses with high invoice volumes. Manual processes are prone to human errors (e.g., data entry mistakes) and delays, while automation ensures real-time accuracy and scalability.
2. What are the key features to look for in automated payment reconciliation software?
Prioritize tools with these features:
- AI-powered matching for instant invoice-payment alignment.
- Real-time alerts for discrepancies, duplicate payments, or fraud.
- Integration capabilities with accounting systems (e.g., QuickBooks, SAP) and payment gateways.
- Customizable workflows to align with your business’s billing cycles and payment methods.
- Audit trails for compliance and dispute resolution.
- Scalability to handle growing transaction volumes without performance loss.
3. Can automated reconciliation handle complex scenarios like partial payments or multiple currencies?
Yes, advanced systems are designed to manage complex cases. For partial payments, they can split matched amounts across multiple invoices and track remaining balances. For multi-currency transactions, they automatically convert currencies using real-time exchange rates and apply correct tax rules. This is critical for global businesses or those with subscription models spanning international customers.
4. How does automation improve cash flow visibility for finance teams?
Automation provides real-time dashboards showing receivables, payables, and cash flow trends. By instantly reconciling payments, it reduces the lag between payment receipt and revenue recognition, allowing teams to forecast cash needs accurately. For instance, alerts for overdue invoices enable proactive collections, while predictive analytics highlight potential shortfalls weeks in advance.
5. What security measures should businesses consider when adopting automated reconciliation tools?
Ensure the software includes:
- End-to-end encryption for data in transit and at rest.
- Role-based access controls to limit sensitive data exposure.
- Fraud detection algorithms to identify anomalies like duplicate payments or mismatched amounts.
- Compliance with standards like PCI DSS for payment data and GDPR for customer information.
- Regular audits to verify system integrity and update security protocols.
6. How can small businesses benefit from automated reconciliation, even with limited resources?
Cloud-based solutions offer cost-effective, scalable options with monthly subscriptions and minimal setup. They reduce the need for in-house accounting teams by automating repetitive tasks, lowering error rates, and accelerating cash flow. For example, a small SaaS company could save 20+ hours monthly by automating recurring payment reconciliations, freeing staff for strategic work.
7. What steps should businesses take to ensure a smooth transition to automated reconciliation?
Follow this roadmap:
- Assess current processes: Identify pain points (e.g., error-prone steps, bottlenecks).
- Choose a compatible tool: Test platforms that integrate with your existing accounting and payment systems.
- Cleanse data: Ensure historical invoices and payment records are accurate before migration.
- Train teams: Provide hands-on training on using the software and interpreting reports.
- Monitor and refine: Use analytics to tweak workflows, such as adjusting matching rules for recurring payments.
- Audit regularly: Compare automated results with manual checks during the transition phase to build trust in the system.